In this post we are going to focus on dbt Core’s components integration with Treasure Data’s solutions.
dbt (data build tool) is an open-source analytics engineering tool primarily focused on data transformation within data engineering systems. It allows users to define, execute, and manage data transformations in a structured and repeatable manner. By leveraging SQL-based transformations and a version-controlled workflow, dbt-Core facilitates the organization and maintenance of complex data transformation processes, enabling more efficient analytics and reporting pipelines. It's widely used to prepare data for analytics, modeling, and visualization, making it a crucial tool in modern data pipelines.
Apart from dbt Cloud, which is a SaaS for Data Ops, dbt Core is an open source command line tool and library that enables data teams to transform data using analytics engineering best practices.
More references:
dbt Core, as a CLI tool, with a bunch of SQL files, configuration files for defining the transformation, requires some external components:
Databases / Data Warehouses, where the data transformation are executed and stored.
- Examples include Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift, and others, allowing you to directly query and transform data stored in these platforms.
- Here, we are going to use Treasure Data (TD)’s Presto Query Engine as demonstration.
Orchestration Tools, where the dbt CLI is executed and scheduled.
Some common orchestration tools are Apache Airflow, Prefect, or Dagster.
Here, we are going to use Treasure Data (TD)’s Treasure Workflow as demonstration.
Besides, there are still some optional but common external components, like:
- Version Control Systems, where the configuration and definition of transformation can be versioned, collaborated, and shared as package importing.
- Data Catalogs and Metadata Management, where the data assets and transformations can be observed, searched, traversed.
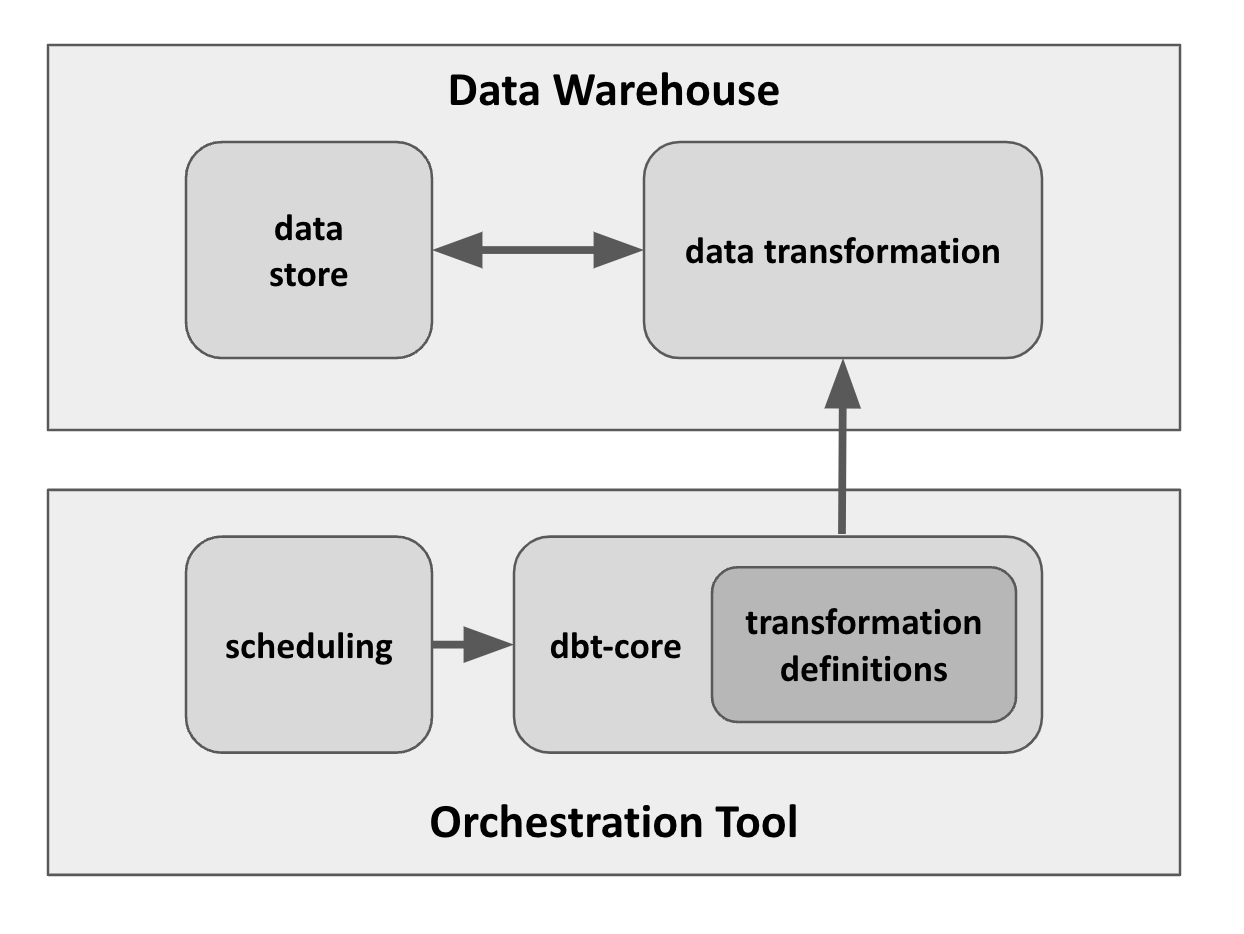 <center>Minimum architecture for dbt-core & external components
<center>Minimum architecture for dbt-core & external components
- TD Toolbelt installation
- digdag installation
- digdag (0.10.5)
- dbt installation (with pip)
- dbt-core (1.6.6)
- dbt-trino (1.6.2)
(The specified versions above are for reference and verified in following examples.)
- Create a connection profile and put into
dbt_profiles/profiles.yml.- Filling your TD API Key into
user. - Decide a default TD database name into
schema.
- Filling your TD API Key into
dbt_project:
target: td
outputs:
td:
type: trino
method: none
user: XXXXXX # TD_API_KEY
database: td-presto # TD presto schema name, not changable
host: api-presto.treasuredata.com # TD presto endpoint
port: 443
schema: dbt_example_db # TD database name
threads: 2
http_scheme: https
prepared_statements_enabled: false- Create the TD database if it has not been created yet. In this example we are calling the database
dbt_example_db.
$ td db:create dbt_example_db- Initiate a dbt project called
dbt_project.
$ dbt init dbt_project --profile dbt_profiles/profiles.yml- The folder structure should look like the following:
├── dbt_profiles
│ └── profiles.yml
└── dbt_project
├── README.md
├── analyses
├── dbt_project.yml
├── macros
├── models
│ └── example
│ ├── my_first_dbt_model.sql
│ ├── my_second_dbt_model.sql
│ └── schema.yml
├── seeds
├── snapshots
└── tests
Add the following configuration to dbt_project/dbt_project.yml, since TD’s schema name td-presto needs be quoted, otherwise, the syntax error will be reported.
quoting:
database: trueThe Treasure Data Presto Query Engine does not support view or materialized view. If you try to use unsupported views the following error displays.
TrinoUserError: Table 'system.metadata.materialized_views' does not exist
To prevent this error, try the following tips:
- Avoid using View and Materialized view as model’s
materializedconfigurations. - Only use following options for materialized configurations:
tableincrementalephemeral
models:
dbt_project:
# Config indicated by + and applies to all files under models/example/
example:
+materialized: table
# +materialized: view ## Don't use view in any cases- Adapter patch to bypass fetching view related catalog.
- Create a macro file
dbt_project/macros/td_adapter_patch/adapters.sql.
- Create a macro file
-- Bypass `materialized_views` to be compatible with TD Presto
-- Related to https://github.com/starburstdata/dbt-trino/issues/298
{% macro trino__list_relations_without_caching(relation) %}
{% call statement('list_relations_without_caching', fetch_result=True) -%}
select
table_catalog as database,
table_name as name,
table_schema as schema,
'table' as table_type
from {{ relation.information_schema() }}.tables
where table_schema = '{{ relation.schema | lower }}'
{% endcall %}
{{ return(load_result('list_relations_without_caching').table) }}
{% endmacro %}Once all the configurations are complete, your first dbt run should look like this:
$ dbt run --profiles-dir dbt_profiles/ --project-dir dbt_project
19:34:57 Running with dbt=1.6.6
19:34:57 Registered adapter: trino=1.6.2
19:34:57 Unable to do partial parsing because a project config has changed
19:34:57 Found 2 models, 4 tests, 0 sources, 0 exposures, 0 metrics, 372 macros, 0 groups, 0 semantic models
19:34:57
19:35:01 Concurrency: 2 threads (target='td')
19:35:01
19:35:01 1 of 2 START sql table model dbt_example_db.my_first_dbt_model ........ [RUN]
19:35:06 1 of 2 OK created sql table model dbt_example_db.my_first_dbt_model ... [SUCCESS in 4.81s]
19:35:06 2 of 2 START sql table model dbt_example_db.my_second_dbt_model ....... [RUN]
19:35:09 2 of 2 OK created sql table model dbt_example_db.my_second_dbt_model .. [SUCCESS in 3.80s]
19:35:09
19:35:09 Finished running 2 table models in 0 hours 0 minutes and 11.92 seconds (11.92s).
19:35:09
19:35:09 Completed successfully
19:35:09
19:35:09 Done. PASS=2 WARN=0 ERROR=0 SKIP=0 TOTAL=2The two executed models should show up in the Treasure Data workbench as tables. 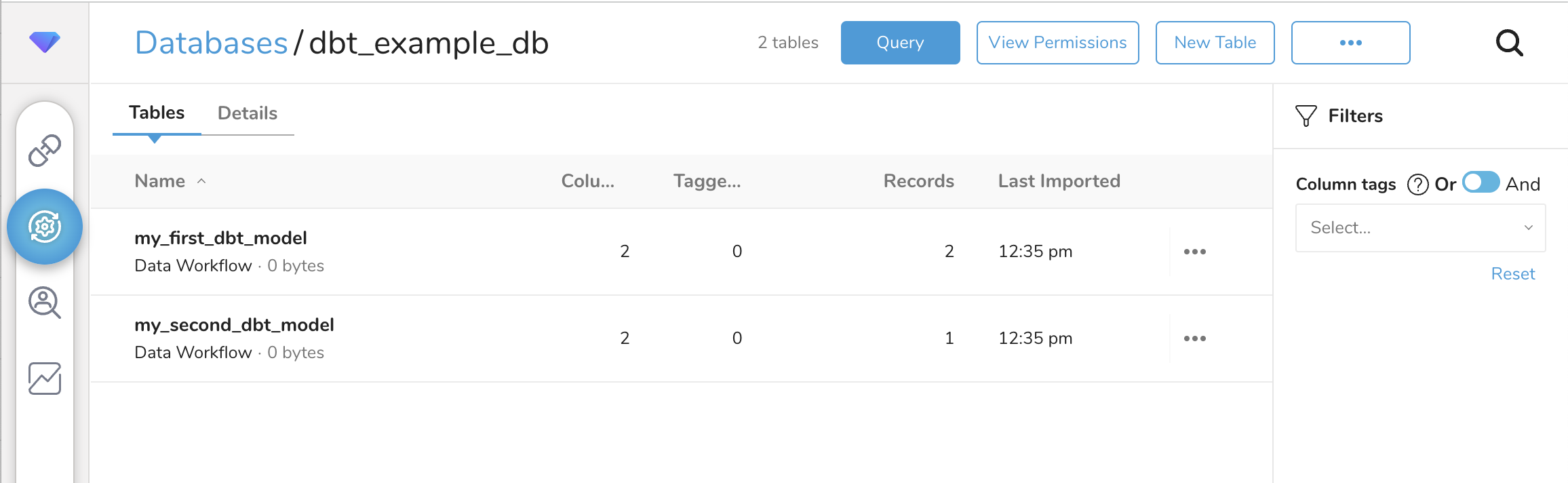
The Treasure Workflow's are an enhanced version of the digdag workflow engine. In order to leverage TD Workflow as the orchestration tool we will need to create a digdag project.
Create a folder for workflow project called
td_wf_projectMove both
dbt_profilesanddbt_projectintotd_wf_projectfolder.Prepare Python Wrapper for invoking dbtRunner in
td_wf_project/scripts/dbt_wrapper.pyso that digdag engine can use `py>`` operator to invoke dbt CLI library.from dbt.cli.main import dbtRunner def invoke(command_list): for cmd in command_list: dbtRunner().invoke([ *(cmd.split()), '--project-dir', './dbt_project', '--profiles-dir', './dbt_profiles', ])Prepare workflow definition in
td_wf_project/dbt_exec_workflow.dig.+dbt_invoke: py>: scripts.dbt_wrapper.invoke _export: command_list: - runNow the folder structure should look like:
td_wf_project ├── dbt_exec_workflow.dig ├── dbt_packages ├── dbt_profiles │ └── profiles.yml ├── dbt_project │ ├── README.md │ ├── analyses │ ├── dbt_project.yml │ ├── macros │ │ └── td_adapter_patch │ │ └── adapters.sql │ ├── models │ │ └── example │ │ ├── my_first_dbt_model.sql │ │ ├── my_second_dbt_model.sql │ │ └── schema.yml │ ├── seeds │ ├── snapshots │ └── tests └── scripts └── dbt_wrapper.pyRun the workflow (
digdag run dbt_exec_workflow.dig) to see results.$ digdag run dbt_exec_workflow.dig ... 22:38:09 Finished running 2 table models in 0 hours 0 minutes and 12.71 seconds (12.71s). 22:38:09 22:38:09 Completed successfully 22:38:09 22:38:09 Done. PASS=2 WARN=0 ERROR=0 SKIP=0 TOTAL=2 Success. Task state is saved at .../dbt_in_td_example/td_wf_project/.digdag/status/20231016T000000+0000 directory. * Use --session <daily | hourly | "yyyy-MM-dd[ HH:mm:ss]"> to not reuse the last session time. * Use --rerun, --start +NAME, or --goal +NAME argument to rerun skipped tasks.
The py> operator in Treasure Workflow is containerized as part of the Custom Scripts feature. To enable this in our project we need to add a few dependencies to our project.
Add runtime pip install in
td_wf_project/scripts/dbt_wrapper.py.import os import sys os.system(f"{sys.executable} -m pip install dbt-core==1.6.6 dbt-trino==1.6.2") from dbt.cli.main import dbtRunner def invoke(command_list): for cmd in command_list: dbtRunner().invoke([ *(cmd.split()), '--project-dir', './dbt_project', '--profiles-dir', './dbt_profiles', ])Add docker option in
td_wf_project/dbt_exec_workflow.dig.+dbt_invoke: py>: scripts.dbt_wrapper.invoke _export: command_list: - run docker: image: "digdag/digdag-python:3.10"
Keeping secrets safe is always important. To do this we are going to follow the How to use Secrets in Custom Scripts docs to protect TD API Key.
Adding an environment variable in
td_wf_project/dbt_exec_workflow.dig.+dbt_invoke: py>: scripts.dbt_wrapper.invoke _export: command_list: - run _env: TD_API_KEY: ${secret:td.apikey} docker: image: "digdag/digdag-python:3.10"Replace the TD API Key, previously set in user
td_wf_project/dbt_profiles/profiles.ymlwith a referring to the environment variable.... user: "{{ env_var('TD_API_KEY') }}" ...
To deploy the workflow to the Treasure Data platform you need to clean up and the push the project.
Clean up before encapsulating package.
- Recommend to add
logsinto the clean targets.
$ dbt clean --profiles-dir dbt_profiles/ --project-dir dbt_project- Recommend to add
Push project to Treasure Workflow.
td workflow push td_wf_project
2023-10-16 16:31:56 -0700: Digdag v0.10.5 Creating .digdag/tmp/archive-3702033545268916293.tar.gz... Archiving dbt_profiles/profiles.yml Archiving dbt_exec_workflow.dig ... Workflows: dbt_exec_workflow.dig Uploaded: id: xxxxxx name: td_wf_project ...
Use td workflow workflows to show all workflows.
- Set secret for Treasure Workflow `td_wf_project` project.
```bash
$ td workflow secrets --project td_wf_project --set td.apikey=XXXXXX
2023-10-16 16:39:58 -0700: Digdag v0.10.5
Secret 'td.apikey' setIn Treasure Data Workbench’s Workflows page, search project name
td_wf_project, then you should seetd.apikeyis set.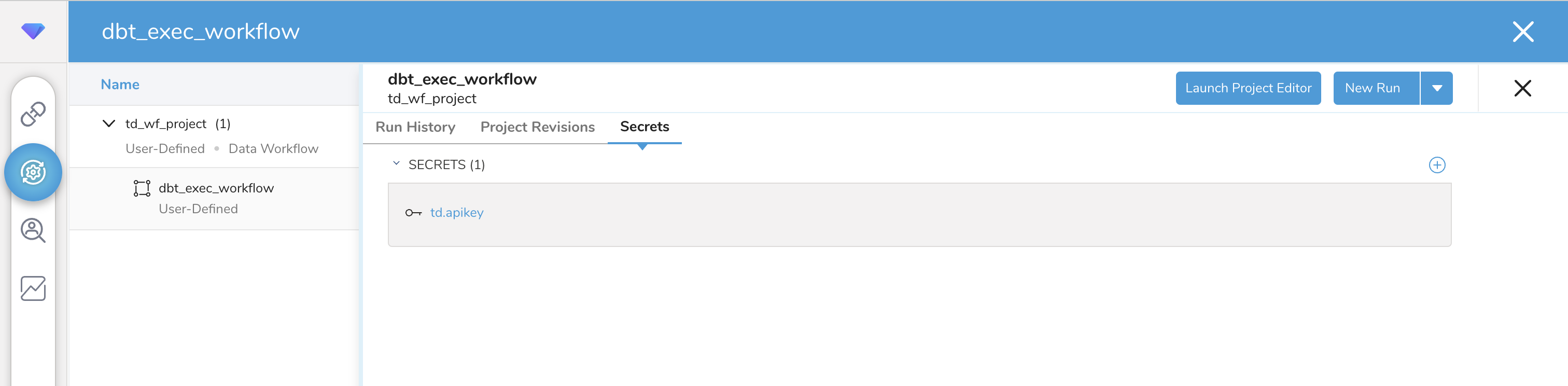
Trigger a “New Run”, the execution results will show in the workflow execution logs.
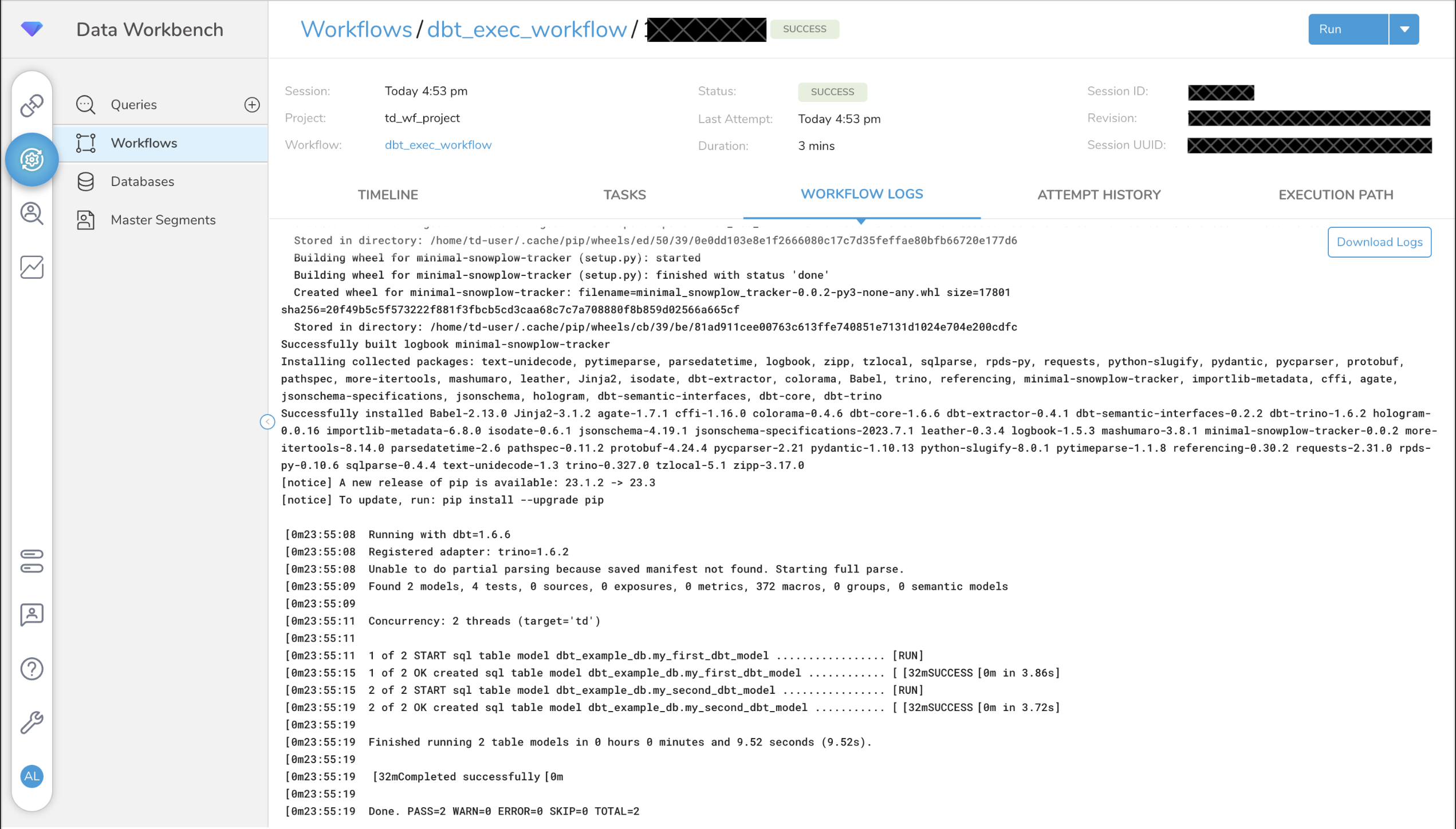
Some additional things you may want to consider doing with the project include:
Add more models or referring other sources in dbt_project.
Add scheduling to periodically trigger workflow and dbt run in
td_wf_project/dbt_exec_workflow.dig, like:timezone: UTC schedule: daily>: 07:00:00
Then simply re-push project by:
$ td workflow push td_wf_projectFrom above steps, a minimum architecture integration is created and deployed. However, there are still many optional augments and tips can greatly empower data operation’s efficiency, maintainability, and observability. Following topics will be covered a future post.
- Invoke with parameters
- Version Control & Documentation
- Observability - log & store results
- Materialized - window refresh for batch processing pipelines
- Package management
- Schema auto evolution