Hivemall Function Reference
Apache Hivemall is a collection of machine learning algorithms and versatile data analytics functions.
Determining Your Version of Hivemall You can determine your version of Hivemall by running the following syntax from the query window within the TD Console:
SELECT HIVEMALL_VERSION()Approximate Functions
APPROX_COUNT_DISTINCT
Signature
approx_count_distinct(column)
approx_distinct(column)Description
APPROX_COUNT_DISTINCT and its alias APPROX_DISTINCT approximately compute the number of unique elements in a column. This function corresponds to Trino(Presto)’s APPROX_DISTINCT. See Hivemall documentation for details.
Natural Language and Text Processing Functions
BASE91
Signature
base91(binary)Description
BASE91 converts the argument from binary to a BASE91 string.
Example
SELECT base91(deflate('aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabbbbccc'));
> AA+=kaIM|WTt!+wbGAAUNBASE91
Signature
unbase91(string)Description
UNBASE91 converts a BASE91 string to a binary.
Example
SELECT inflate(unbase91(base91(deflate('aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabbbbccc'))));
> aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabbbbcccIS_STOPWORD
Signature
is_stopword(string word)Description
IS_STOPWORD determines whether a word is an English stop word or not. Stop words are words that are filtered out before or after the processing of text.
NORMALIZE_UNICODE
Signature
normalize_unicode(string str [, string form])Description
NORMALIZE_UNICODE transforms str to the specified normalization form. The form takes one of NFC (default), NFD, NFKC, or NFKD.
Example
select normalize_unicode('ハンカクカナ','NFKC');
ハンカクカナ
select normalize_unicode('㈱㌧㌦Ⅲ','NFKC');
(株)トンドルIIISINGULARIZE
Signature
singularize(string word)Description
SINGULARIZE returns the singular form of a given English word. For more information, see Hivemall User Guide.
SPLIT_WORDS
Signature
split_words(string query [, string regex])Description
SPLIT_WORDS returns an array that contains split strings.
WORD_NGRAMS
Signature
word_ngrams(array<string> words, int minSize, int maxSize)Description
WORD_NGRAMS returns list of n-grams where minSize <= n <= maxSize. For more information, see Hivemall User Guide.
TOKENIZE
Signature
tokenize(string englishText [, boolean toLowerCase])Description
TOKENIZE returns the words in an array.
TOKENIZE_JA
Signature
tokenize_ja(String line [, const string mode = "normal", const list<string> stopWords, const list<string> stopTags, const array<string> userDict (or string userDictURL)])Description
TOKENIZE_JA returns tokenized strings in an array. You can use a given predefined dictionary as an array or as a URL to a file uploaded to somewhere like Amazon S3. See Hivemall User Guide
If you have restricted access in your Amazon S3, you must allow access to it from Treasure Data. The TOKENIZE_JA function can be used to allow access even if your S3 environment is restricted. The static IPs used to allow access must be the same as those used for your Result Workers. If necessary, contact TD Support.
If your Amazon S3 does not restrict access, no configuration using the TOKENIZE_JA function is required.
When your CSV file for the custom dictionary has duplicate entries, your job fails as an
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDFArgumentException error. It is important to resolve the duplication in advance.
Example
select tokenize_ja("kuromojiを使った分かち書きのテストです。第二引数にはnormal/search/extendedを指定できます。デフォルトではnormalモードです。");
["kuromoji","使う","分かち書き","テスト","第","二","引数","normal","search","extended","指定","デフォルト","normal"," モード"]
select tokenize_ja("関西国際空港", "normal", null, null,
array("関西国際空港,関西 国際 空港,カンサイ コクサイ クウコウ,カスタム名詞"));
["関西","国際","空港"]
-- stoptags_exclude is useful for an include rule of part-of-speech information
select tokenize_ja("kuromojiを使った分かち書きのテストです。", "normal", array("kuromoji"), stoptags_exclude(array("名詞")));
["分かち書き","テスト"]
-- using pre-defined library
select tokenize_ja("関西国際空港", "normal", null, null, "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/atilika/kuromoji/909fd6b32bf4e9dc86b7599de5c9b50ca8f004a1/kuromoji-core/src/test/resources/userdict.txt");
["関西","国際","空港"]You can get Part-of-Speech (PoS) information using -pos option as follows:
WITH tmp as (
select
tokenize_ja('kuromojiを使った分かち書きのテストです。','-mode search -pos') as r
)
select
r.tokens,
r.pos,
r.tokens[0] as token0,
r.pos[0] as pos0
from
tmp;| tokens | pos | token0 | pos0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ["kuromoji","使う","分かち書き","テスト"] | ["名詞-一般","動詞-自立","名詞-一般","名詞-サ変接続"] | kuromoji | 名詞-一般 |
You can get the complete list of stopTags by
select stoptags_exclude(array());TOKENIZE_JA_NEOLOGD
Signature
tokenize_ja_neologd(String line [, const string mode = "normal", const list<string> stopWords, const list<string> stopTags, const array<string> userDict (or string userDictURL)])Description
TOKENIZE_JA_NEOLOGD returns tokenized strings in an array by using the NEologd dictionary.
mecab-ipadic-NEologd is a customized system dictionary for MeCab; it includes new words that are extracted from many different language resources on the Web. For more details, see Hive Japanese NLP UDFs with NEologd
Example
select tokenize_ja_neologd(); -- returns current UDF version with corresponding NEologd version date
["0.1.0-20180524"]
select tokenize_ja_neologd("彼女はペンパイナッポーアッポーペンと恋ダンスを踊った。");
["彼女","ペンパイナッポーアッポーペン","恋ダンス","踊る"]TOKENIZE_CN
Signature
tokenize_cn(string line, optional const array<string> stopWords)Description
Simplified Chinese text tokenizer UDF uses SmartChineseAnalyzer.
Example
select tokenize_cn("Smartcn为Apache2.0协议的开源中文分词系统,Java语言编写,修改的中科院计算所ICTCLAS分词系统。");
[smartcn, 为, apach, 2, 0, 协议, 的, 开源, 中文, 分词, 系统, java, 语言, 编写, 修改, 的, 中科院, 计算, 所, ictcla, 分词, 系统]TOKENIZE_KO
Signature
tokenize_ko(
String line [, const string mode = "discard" (or const string opts),
const array<string> stopWords,
const array<string>
stopTags,
const array<string> userDict (or const string userDictURL)]
) - returns tokenized strings in array<string>Description
The Korean tokenizer internally uses lucene-analyzers-nori for tokenization.
For additional usage help:
select tokenize_ko("", "-help");
usage: tokenize_ko(String line [, const string mode = "discard" (or const
string opts), const array<string> stopWords, const array<string>
stopTags, const array<string> userDict (or const string
userDictURL)]) - returns tokenized strings in array<string> [-help]
[-mode <arg>] [-outputUnknownUnigrams]
-helpShow function help
-mode <arg> The tokenization mode. One of ['node', 'discard'
(default), 'mixed']
-outputUnknownUnigrams outputs unigrams for unknown words.For the 2nd argument, instead of mode, you can use options starting with -. For detailed options, refer to the Lucene API document. none, discord (default), or mixed are supported for the mode argument.
Examples
-- show version of lucene-analyzers-nori
select tokenize_ko();
> 8.8.2
select tokenize_ko('중요한 새 기능을 개발해줘서 정말 고마워요!');
> ["중요","기능","개발","주","고맙"]
-- explicitly using default options
select tokenize_ko('중요한 새 기능을 개발해줘서 정말 고마워요!', '-mode discard',
-- stopwords (null to use default)
-- see https://github.com/apache/incubator-hivemall/blob/master/nlp/src/main/resources/hivemall/nlp/tokenizer/ext/stopwords-ko.txt
null,
-- stoptags
-- see https://lucene.apache.org/core/8_8_2/analyzers-nori/org/apache/lucene/analysis/ko/POS.Tag.html
array(
'E', -- Verbal endings
'IC', -- Interjection
'J', -- Ending Particle
'MAG', -- General Adverb
'MAJ', -- Conjunctive adverb
'MM', -- Determiner
'SP', -- Space
'SSC', -- Closing brackets
'SSO', -- Opening brackets
'SC', -- Separator
'SE', -- Ellipsis
'XPN', -- Prefix
'XSA', -- Adjective Suffix
'XSN', -- Noun Suffix
'XSV', -- Verb Suffix
'UNA', -- Unknown
'NA', -- Unknown
'VSV' -- Unknown
)
);
> ["중요","기능","개발","주","고맙"]
-- None mode, without General Adverb (MAG)
select tokenize_ko('중요한 새 기능을 개발해줘서 정말 고마워요!',
-- No decomposition for compound.
'-mode none',
-- stopwords (null to use default)
null,
array(
'E', -- Verbal endings
'IC', -- Interjection
'J', -- Ending Particle
-- 'MAG', -- General Adverb
'MAJ', -- Conjunctive adverb
'MM', -- Determiner
'SP', -- Space
'SSC', -- Closing brackets
'SSO', -- Opening brackets
'SC', -- Separator
'SE', -- Ellipsis
'XPN', -- Prefix
'XSA', -- Adjective Suffix
'XSN', -- Noun Suffix
'XSV', -- Verb Suffix
'UNA', -- Unknown
'NA', -- Unknown
'VSV' -- Unknown
)
);
> ["중요","기능","개발","줘서","정말","고마워요"]
-- discard mode: Decompose compounds and discards the original form (default).
-- https://lucene.apache.org/core/8_8_2/analyzers-nori/org/apache/lucene/analysis/ko/KoreanTokenizer.DecompoundMode.html
select tokenize_ko('중요한 새 기능을 개발해줘서 정말 고마워요!', '-mode discard');
> ["중요","기능","개발","주","고맙"]
-- default stopward (null), with stoptags
select tokenize_ko('중요한 새 기능을 개발해줘서 정말 고마워요!', '-mode discard', null, array('E', 'VV'));
> ["중요","하","새","기능","을","개발","하","주","정말","고맙"]
-- mixed mode: Decompose compounds and keeps the original form.
select tokenize_ko('중요한 새 기능을 개발해줘서 정말 고마워요!', 'mixed');
> ["중요","기능","개발","줘서","주","고마워요","고맙"]
select tokenize_ko('중요한 새 기능을 개발해줘서 정말 고마워요!', '-mode mixed');
> ["중요","기능","개발","줘서","주","고마워요","고맙"]
-- node mode: No decomposition for compound.
select tokenize_ko('중요한 새 기능을 개발해줘서 정말 고마워요!', '-mode none');
> ["중요","기능","개발","줘서","고마워요"]
select tokenize_ko('Hello, world.', '-mode none');
> ["hello","world"]
select tokenize_ko('Hello, world.', '-mode none -outputUnknownUnigrams');
> ["h","e","l","l","o","w","o","r","l","d"]
select tokenize_ko('나는 C++ 언어를 프로그래밍 언어로 사랑한다.', '-mode discard');
> ["나","c","언어","프로그래밍","언어","사랑"]
select tokenize_ko('나는 C++ 언어를 프로그래밍 언어로 사랑한다.', '-mode discard', array(), null);
> ["나","는","c","언어","를","프로그래밍","언어","로","사랑","하","ᆫ다"]
-- default stopward (null), default stoptags (null)
select tokenize_ko('나는 C++ 언어를 프로그래밍 언어로 사랑한다.', '-mode discard');
select tokenize_ko('나는 C++ 언어를 프로그래밍 언어로 사랑한다.', '-mode discard', null, null);
> ["나","c","언어","프로그래밍","언어","사랑"]
-- no stopward (empty array), default stoptags (null)
select tokenize_ko('나는 C++ 언어를 프로그래밍 언어로 사랑한다.', '-mode discard', array());
select tokenize_ko('나는 C++ 언어를 프로그래밍 언어로 사랑한다.', '-mode discard', array(), null);
> ["나","c","언어","프로그래밍","언어","사랑"]
-- no stopward (empty array), no stoptags (emptry array), custom dict
select tokenize_ko('나는 C++ 언어를 프로그래밍 언어로 사랑한다.', '-mode discard', array(), array(), array('C++'));
> ["나","는","c++","언어","를","프로그래밍","언어","로","사랑","하","ᆫ다"]
> -- default stopward (null), default stoptags (null), custom dict
select tokenize_ko('나는 C++ 언어를 프로그래밍 언어로 사랑한다.', '-mode discard', null, null, array('C++'));
> ["나","c++","언어","프로그래밍","언어","사랑"]Custom Dictionary
The fifth argumentuserDictURL enables you to register a user-defined custom dictionary placed in http/https accessible external site. Learn more about the custom dictionary format here.
`select tokenize_ko('나는 c++ 프로그래밍을 즐긴다.', '-mode discard', null, null, 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/apache/lucene/main/lucene/analysis/nori/src/test/org/apache/lucene/analysis/ko/userdict.txt');
> ["나","c++","프로그래밍","즐기"]Info
The custom dictionary must be be accessible through HTTP or HTTPS.
Treasure Data recommends that it be compressed using gzip with a .gz suffix because the maximum dictionary size is limited to 32MB and the read timeout is set to 60 seconds.
The connection must be established in 10 seconds.
GeoSpatial User Defined Functions
TILE
Signature
tile(double lat, double lon, int zoom)Description
TILE returns a tile number in xtile(lon,zoom) + ytile(lat,zoom) * 2^z. The tile number is in the range [0,2^2z]. For more information, see Hivemall User Guide
HAVERSINE_DISTANCE
Signature
haversine_distance(double lat1, double lon1, double lat2, double lon2, [const boolean mile=false])Description
HAVERSINE_DISTANCE returns the Haversine distance between two Geo locations.For more information, see Hivemall User Guide.
Example
-- Tokyo (lat: 35.6833, lon: 139.7667), Osaka (lat: 34.6603, lon: 135.5232)
select
haversine_distance(35.6833, 139.7667, 34.6603, 135.5232) as km,
haversine_distance(35.6833, 139.7667, 34.6603, 135.5232, true) as mile;
402.09212137829684 249.8484608500711Aggregate Functions
MAJORITY_VOTE
Signature
majority_vote(Primitive x) Description
Returns the most frequent value.
Example
WITH data as (
select
explode(array('1', '2', '2', '2', '5', '4', '1', '2')) as k
)
select
majority_vote(k) as k
from
data;
> 2MAX_BY
Signature
max_by(x, y)Description
Returns the value of x associated with the maximum value of y over all input values.
Example
WITH data as (
select 'jake' as name, 18 as age
union all
select 'tom' as name, 64 as age
union all
select 'lisa' as name, 32 as age
)
select
max_by(name, age) as name
from
data;
> tomMIN_BY
Signature
min_by(x, y)Description
Returns the value of x associated with the minimum value of y over all input values.
Example
WITH data as (
select 'jake' as name, 18 as age
union all
select 'tom' as name, 64 as age
union all
select 'lisa' as name, 32 as age
)
select
min_by(name, age) as name
from
data;
> jake Array Functions
ARANGE
Signature
arange([int start=0, ] int stop, [int step=1])Description
Return evenly spaced values within a given interval.
Example
select arange(5), arange(1, 5), arange(1, 5, 1), arange(0, 5, 1);
> [0,1,2,3,4] [1,2,3,4] [1,2,3,4] [0,1,2,3,4]
select arange(1, 6, 2);
> 1, 3, 5
select arange(-1, -6, 2);
> -1, -3, -5ARGMAX
Signature
argmax(array<T> a)Description
Return the first index of the maximum value
Example
select argmax(array(5,2,0,1));
> 0ARGMIN
Signature
argmin(array<T> a)Description
Return the first index of the minimum value
Example
SELECT argmin(array(5,2,0,1));
> 2ARGRANK
Signature
argrank(array<ANY> a)Description
Return the indices that would sort an array.
Example
select argrank(array(5,2,0,1)), argsort(argsort(array(5,2,0,1)));
> [3, 2, 0, 1] [3, 2, 0, 1]ARGSORT
Signature
argsort(array<ANY> a)Description
Return the indices that would sort an array.
Example
select argsort(array(5,2,0,1));
> 2, 3, 1, 0ARRAY_APPEND
Signature
array_append(array<T> arr, T elem)Description
Append an element to the end of an array.
Example
SELECT array_append(array(1,2),3);
> 1,2,3
SELECT array_append(array('a','b'),'c');
> "a","b","c"ARRAY_AVG
Signature
array_avg(array<number>)Description
Returns an array<double> where each element is the mean of a set of numbers. This is an aggregate function.
Example
WITH input as (
select array(1.0, 2.0, 3.0) as nums
UNION ALL
select array(2.0, 3.0, 4.0) as nums
)
select
array_avg(nums)
from
input
> ["1.5","2.5","3.5"]6.8. ARRAY_CONCAT
Signature
array array_concat(array<ANY> x1, array<ANY> x2, ..)Description
The ARRAY_CONCAT function returns a concatenated array.
Example
select array_concat(array(1),array(2,3))
> [1,2,3]ARRAY_FLATTEN
Signature
array_flatten(array<array<ANY>>)Description
Returns an array with the elements flattened.
Example
SELECT array_flatten(array(array(1,2,3),array(4,5),array(6,7,8)));
> [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]ARRAY_INTERSECT
Signature
array_intersect(array<ANY> x1, array<ANY> x2, ..)Description
The ARRAY_INTERSECT function returns an intersect of given arrays.
Example
select array_intersect(array(1,3,4),array(2,3,4),array(3,5))
> [3]ARRAY_REMOVE
Signature
array_remove(array<int|text> original, int|text|array<int> target)Description
ARRAY_REMOVE returns an array where the target is removed from the original array.
Example
select array_remove(array(1,null,3),array(1));
> [null,3]
select array_remove(array("aaa","bbb"),"bbb");
> ["aaa"]ARRAY_SLICE
Signature
array_slice(array<ANY> values, int offset [, int length])Description
Slices the given array by the given offset and length parameters.
Example
SELECT
array_slice(array(1,2,3,4,5,6),2,4),
array_slice(
array("zero", "one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six", "seven", "eight", "nine", "ten"),
0, -- offset
2 -- length
),
array_slice(
array("zero", "one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six", "seven", "eight", "nine", "ten"),
6, -- offset
3 -- length
),
array_slice(
array("zero", "one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six", "seven", "eight", "nine", "ten"),
6, -- offset
10 -- length
),
array_slice(
array("zero", "one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six", "seven", "eight", "nine", "ten"),
6 -- offset
),
array_slice(
array("zero", "one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six", "seven", "eight", "nine", "ten"),
-3 -- offset
),
array_slice(
array("zero", "one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six", "seven", "eight", "nine", "ten"),
-3, -- offset
2 -- length
);
> [3,4]
> ["zero","one"]
> ["six","seven","eight"]
> ["six","seven","eight","nine","ten"]
> ["six","seven","eight","nine","ten"]
> ["eight","nine","ten"]
> ["eight","nine"]ARRAY_SUM
Signature
array_sum(array<NUMBER>)Description
ARRAY_SUM returns an array where each element is summed up.
Example
WITH input as (
select array(1.0, 2.0, 3.0) as nums
UNION ALL
select array(2.0, 3.0, 4.0) as nums
)
select
array_sum(nums)
from
input
> ["3.0","5.0","7.0"]ARRAY_TO_STR
Signature
array_to_str(array arr [, string sep=','])Description
Converts an array to a string using a separator.
Example
SELECT array_to_str(array(1,2,3),'-');
> 1-2-3ARRAY_UNION
Signature
array_union(array1, array2, ...)Description
Returns the union of a set of arrays.
Example
SELECT array_union(array(1,2),array(1,2));
> [1,2]
SELECT array_union(array(1,2),array(2,3),array(2,5));
> [1,2,3,5]CONDITIONAL_EMIT
Signature
conditional_emit(array<boolean> conditions, array<primitive> features)Description
Emit the features of a row according to various conditions.
Example
WITH INPUT AS(
SELECT
ARRAY(TRUE,
FALSE,
TRUE) AS conditions,
ARRAY("one",
"two",
"three") AS features
UNION
ALL SELECT
ARRAY(TRUE,
TRUE,
FALSE) AS conditions,
ARRAY("four",
"five",
"six") AS features
) SELECT
conditional_emit(
conditions,
features
)
FROM
INPUT
;ELEMENT_AT
Signature
element_at(array<T> list, int pos)Description
Returns an element at the given position
Example
SELECT element_at(array(1,2,3,4),0);
> 1
SELECT element_at(array(1,2,3,4),-2);
> 3FIRST_ELEMENT
Description
Returns the first element in an array.
Example
SELECT first_element(array('a','b','c'));
> a
SELECT first_element(array());
> NULLFLOAT_ARRAY
Signature
float_array(nDims)Description
Returns an array<float> of nDims elements.
LAST_ELEMENT
Description
Return the last element in an array.
Example
SELECT last_element(array('a','b','c'));
> cSELECT_K_BEST
Signature
select_k_best(array<number> array, const array<number> importance, const int k)Description
Returns selected top-k elements as array
SORT_AND_UNIQ_ARRAY
Signature
sort_and_uniq_array(array<int>)Description
SORT_AND_UNIQ_ARRAY takes an array of type int and returns a sorted array in a natural order with duplicate elements eliminated.
Example
SELECT sort_and_uniq_array(array(3,1,1,-2,10));
> [-2,1,3,10]SUBARRAY
Signature
subarray(array<int> orignal, int fromIndex, int toIndex)Description
SUBARRAY returns a slice of the original array between the inclusive fromIndex and the exclusive toIndex.
Example
SELECT subarray(array(1,2,3,4,5,6), 2,4)
> [3,4]SUBARRAY_ENDWITH
Signature
subarray_endwith(array<int|text> original, int|text key)Description
SUBARRAY_ENDWITH returns an array that ends with the specified key
Example
SELECT subarray_endwith(array(1,2,3,4), 3);
> [1,2,3]SUBARRAY_STARTWITH
Signature
subarray_startwith(array<int|text> original, int|text key)Description
SUBARRAY_STARTWITH returns an array that starts with the specified key.
Example
SELECT subarray_startwith(array(1,2,3,4), 2);
> [2,3,4]TO_STRING_ARRAY
Signature
to_string_array(array<ANY>)Description
TO_STRING_ARRAY returns an array of strings.
Example
SELECT to_string_array(array(1.0,2.0,3.0));
> ["1.0","2.0","3.0"]TO_ORDERED_LIST
Signature
to_ordered_list(PRIMITIVE value [, PRIMITIVE key, const string options])
to_ordered_list(value, key [, const string options])Description
TO_ORDERED_LIST returns list of values sorted by value itself or specific key. For more information, see Hivemall user guide.
Example
WITH t as (
SELECT 5 as key, 'apple' as value
UNION ALL
SELECT 3 as key, 'banana' as value
UNION ALL
SELECT 4 as key, 'candy' as value
UNION ALL
SELECT 2 as key, 'donut' as value
UNION ALL
SELECT 3 as key, 'egg' as value
)
SELECT -- expected output
to_ordered_list(value, key, '-reverse'), -- [apple, candy, (banana, egg | egg, banana), donut] (reverse order)
to_ordered_list(value, key, '-k 2'), -- [apple, candy] (top-k)
to_ordered_list(value, key, '-k 100'), -- [apple, candy, (banana, egg | egg, banana), dunut]
to_ordered_list(value, key, '-k 2 -reverse'), -- [donut, (banana | egg)] (reverse top-k = tail-k)
to_ordered_list(value, key), -- [donut, (banana, egg | egg, banana), candy, apple] (natural order)
to_ordered_list(value, key, '-k -2'), -- [donut, (banana | egg)] (tail-k)
to_ordered_list(value, key, '-k -100'), -- [donut, (banana, egg | egg, banana), candy, apple]
to_ordered_list(value, key, '-k -2 -reverse'), -- [apple, candy] (reverse tail-k = top-k)
to_ordered_list(value, '-k 2'), -- [egg, donut] (alphabetically)
to_ordered_list(key, '-k -2 -reverse'), -- [5, 4] (top-2 keys)
to_ordered_list(key), -- [2, 3, 3, 4, 5] (natural ordered keys)
to_ordered_list(value, key, '-k 2 -kv_map'), -- {4:"candy",5:"apple"}
to_ordered_list(value, key, '-k 2 -vk_map') -- {"candy":4,"apple":5}
FROM
t;Bitset Functions
BITS_COLLECT
Signature
bits_collect(int|long x)Description
BITS_COLLECT returns a bit set in array. This function is an aggregate function.
BITS_OR
Signature
bits_or(array<long> b1, array<long> b2, ..)Description
BITS_OR returns a logical OR given bit sets.
Example
SELECT unbits(bits_or(to_bits(array(1,4)),to_bits(array(2,3))));
> [1,2,3,4]TO_BITS
Signature
to_bits(int[] indexes)Description
TO_BITS returns an bitset representation if the given indexes in long[].
Example
SELECT to_bits(array(1,2,3,128));
> [14,-9223372036854775808]UNBITS
Signature
unbits(long[] bitset)Description
UNBITS returns a long array of the given bitset representation
Example
SELECT unbits(to_bits(array(1,4,2,3)));
> [1,2,3,4]Compression Functions
DEFLATE
Signature
deflate(TEXT data [, const int compressionLevel])Description
DEFLATE returns a compressed BINARY object by using Deflater. The compression level must be within the range [-1,9].
Example
SELECT base91(deflate('aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabbbbccc'));
> AA+=kaIM|WTt!+wbGAAINFLATE
Signature
inflate(BINARY compressedData)Description
INFLATE returns a decompressed STRING by using Inflater
Example
SELECT inflate(unbase91(base91(deflate('aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabbbbccc'))));
> aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabbbbcccDatetime Functions
SESSIONIZE
Signature
sessionize(long timeInSec, long thresholdInSec [, String subject])Description
SESSIONIZE Returns a UUID string of a session.
Example
SELECT
sessionize(time, 3600, ip_addr) as session_id,
time, ip_addr
FROM (
SELECT time, ipaddr
FROM weblog
DISTRIBUTE BY ip_addr, time SORT BY ip_addr, time DESC
) t1;JSON Functions
TO_JSON
Signature
to_json(object)Description
TO_JSON returns JSON string of given object.
Example
select to_json(ARRAY('a', 'b', 'c'));
'["a","b","c"]'FROM_JSON
Signature
from_json(STRING json, const string type)Description
FROM_JSON converts a given JSON string into an object of the specified type.
Example
select from_json('["a","b","c"]', 'array<string>');
["a","b","c"]Map Functions
MAP_EXCLUDE_KEYS
Signature
map_exclude_keys(Map<K,V> map, array<K> filteringKeys)Description
MAP_EXCLUDE_KEYS returns the filtered entries of a map that excludes specified keys
Example
SELECT map_exclude_keys(map(1,'one',2,'two',3,'three'),array(2,3));
> {1:"one"}MAP_GET
Signature
map_get(MAP<K> a, K n)Description
Return the value corresponding to the key in the map.
Example
WITH tmp as (
SELECT "one" as key
UNION ALL
SELECT "two" as key
)
SELECT map_get(map("one",1,"two",2),key)
FROM tmp;
> 1
> 2MAP_GET_SUM
Signature
map_get_sum(map<int,float> src, array<int> keys)Description
MAP_GET_SUM returns sum of values that are retrieved by keys.
11.4. MAP_INCLUDE_KEYS
Signature
map_include_keys(Map<K,V> map, array<K> filteringKeys)Description
MAP_INCLUDE_KEYS returns the filtered entries of a map having specified keys.
Example
SELECT map_include_keys(map(1,'one',2,'two',3,'three'),array(2,3));
> {2:"two",3:"three"} MAP_KEY_VALUES
Signature
array<named_struct<key,value>> map_key_values(Map<K, V> map)Description
MAP_KEY_VALUES returns a array of key-value pairs in array<named_struct<key,value>>.
Example
SELECT map_key_values(map("one",1,"two",2));
> [{"key":"one","value":1},{"key":"two","value":2}]MAP_ROULETTE
Signature
map_roulette(map<key, number> [, integer seed])Description
Return key by weighted random selection.
Example
-- returns key by weighted random selection
SELECT
map_roulette(to_map(a, b)) -- 25% Tom, 21% Zhang, 54% Wang
FROM ( -- see https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/HIVE-17406
select 'Wang' as a, 54 as b
union all
select 'Zhang' as a, 21 as b
union all
select 'Tom' as a, 25 as b
) tmp;
> Wang
-- Weight random selection with using filling nulls with the average value
SELECT
map_roulette(map(1, 0.5, 'Wang', null)), -- 50% Wang, 50% 1
map_roulette(map(1, 0.5, 'Wang', null, 'Zhang', null)) -- 1/3 Wang, 1/3 1, 1/3 Zhang
-- NULL will be returned if every key is null
SELECT
map_roulette(map()),
map_roulette(map(null, null, null, null));
> NULL NULL
-- Return NULL if all weights are zero
SELECT
map_roulette(map(1, 0)),
map_roulette(map(1, 0, '5', 0))
> NULL NULL
-- map_roulette does not support non-numeric weights or negative weights.
SELECT map_roulette(map('Wong', 'A string', 'Zhao', 2));
> HiveException: Error evaluating map_roulette(map('Wong':'A string','Zhao':2))
SELECT map_roulette(map('Wong', 'A string', 'Zhao', 2));
> UDFArgumentException: Map value must be greather than or equals to zero: -2MAP_TAIL_N
Signature
map_tail_n(map SRC, int N)Description
MAP_TAIL_N returns the last N elements from a sorted array of SRC.
MERGE_MAPS
Signature
merge_maps(Map x)Description
MERGE_MAPS returns a map that contains the union of an aggregation of maps. An existing value of a key can be replaced with the other duplicate key entry.
Example
SELECT
merge_maps(m)
FROM (
SELECT map('A',10,'B',20,'C',30)
UNION ALL
SELECT map('A',10,'B',20,'C',30)
) t;TO_MAP
Signature
to_map(key, value)Description
TO_MAP converts two aggregated columns into a key-value map.
Example
WITH input as (
select 'aaa' as key, 111 as value
UNION all
select 'bbb' as key, 222 as value
)
select to_map(key, value)
from input;
> {"bbb":222,"aaa":111}TO_ORDERED_MAP
Signature
to_ordered_map(key, value [, const boolean reverseOrder=false])Description
TO_ORDERED_MAP converts two aggregated columns into an ordered key-value map.
Example
with t as (
select 10 as key, 'apple' as value
union all
select 3 as key, 'banana' as value
union all
select 4 as key, 'candy' as value
)
select
to_ordered_map(key, value, true), -- {10:"apple",4:"candy",3:"banana"} (reverse)
to_ordered_map(key, value, 1), -- {10:"apple"} (top-1)
to_ordered_map(key, value, 2), -- {10:"apple",4:"candy"} (top-2)
to_ordered_map(key, value, 3), -- {10:"apple",4:"candy",3:"banana"} (top-3)
to_ordered_map(key, value, 100), -- {10:"apple",4:"candy",3:"banana"} (top-100)
to_ordered_map(key, value), -- {3:"banana",4:"candy",10:"apple"} (natural)
to_ordered_map(key, value, -1), -- {3:"banana"} (tail-1)
to_ordered_map(key, value, -2), -- {3:"banana",4:"candy"} (tail-2)
to_ordered_map(key, value, -3), -- {3:"banana",4:"candy",10:"apple"} (tail-3)
to_ordered_map(key, value, -100) -- {3:"banana",4:"candy",10:"apple"} (tail-100)
from t;MapReduce Functions
ROWID
Signature
string rowid()Description
ROWID returns a generated row id of a form {TASKID}–{SEQUENCENUMBER}
Example
SELECT rowid() as rowid, col1, col2 FROM inputROWNUM
Signature
long rownum()Description
ROWNUM returns a generated row number sprintf(%d%04d,sequence,taskId) in a long.
Example
SELECT rownum() as rowid, col1, col2 FROM inputMath Function
INFINITY
Signature
double infinity()Description
INFINITY returns the constant representing positive infinity.
IS_FINITE
Signature
boolean is_finite(number x)Description
IS_FINITE determines if x is finite.
Example
SELECT is_finite(333), is_finite(infinity());
> true falseIS_INFINITE
Signature
boolean is_infinite(number x)Description
IS_INFINITE determines if x is infinite.
Example
SELECT is_infinite(333), is_infinite(infinity());
> false true IS_NAN
Signature
boolean is_nan(number x)Description
IS_NAN determines if x is not-a-number.
Example
SELECT is_nan(333), is_nan(nan());
> false trueL2_NORM
Signature
double l2_norm(number x)Description
L2_NORM return an L2 norm of the given input x.
Example
WITH input as (
select generate_series(1,3) as v
)
select l2_norm(v) as l2norm
from input;
> 19.621416870348583 = sqrt(1^2+2^2+3^2))NAN
Signature
double nan()Description
NAN returns the constant representing not-a-number.
Example
SELECT nan(), is_nan(nan());
> NaN trueSIGMOID
Signature
sigmoid(x)Description
SIGMOID returns 1.0 / (1.0 + exp(-x)).
Example
WITH input as (
SELECT 3.0 as x
UNION ALL
SELECT -3.0 as x
)
select
1.0 / (1.0 + exp(-x)),
sigmoid(x)
from
input;
> 0.04742587317756678 0.04742587357759476
> 0.9525741268224334 0.9525741338729858Vector and Matrix Functions
TRANSPOSE_AND_DOT
Signature
transpose_and_dot(array<number> X, array<number> Y)Description
TRANSPOSE_AND_DOT returns dot(X.T, Y) as array<array<double>>, shape = (X.#cols, Y.#cols).
For example, the transpose of an m × n matrix A is the n × m matrix AT whose columns are the rows of A.
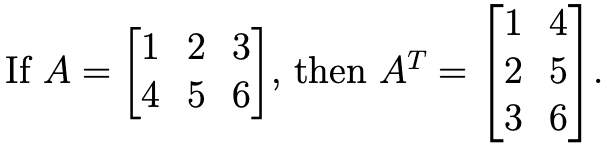
Example
WITH input as (
select array(1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0) as x, array(1, 2) as y
UNION ALL
select array(2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0) as x, array(1, 2) as y
)
select
transpose_and_dot(x, y) as xy,
transpose_and_dot(y, x) as yx
from
input;
> [["3.0","6.0"],["5.0","10.0"],["7.0","14.0"],["9.0","18.0"]] [["3.0","5.0","7.0","9.0"],["6.0","10.0","14.0","18.0"]]VECTOR_ADD
Signature
vector_add(array<NUMBER> x, array<NUMBER> y)Description
VECTOR_ADD performs a vector ADD operation. This call appends the specified element to the end of this vector.
Example
SELECT vector_add(array(1.0,2.0,3.0), array(2, 3, 4));
> [3.0,5.0,7.0]VECTOR_DOT
Signature
vector_dot(array<NUMBER> x, array<NUMBER> y)Description
VECTOR_DOT performs a vector dot product calculation.
The dot product is the sum of the products of the corresponding entries of the two sequences of numbers. Geometrically, it is the product of the Euclidean magnitudes of the two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them. These definitions are equivalent when using Cartesian coordinates.
Example
SELECT vector_dot(array(1.0,2.0,3.0),array(2.0,3.0,4.0));
> 20
SELECT vector_dot(array(1.0,2.0,3.0),2);
> [2.0,4.0,6.0]Sanity Check Functions
ASSERT
Signature
assert(boolean condition [, string errMsg])Description
ASSERT throws HiveException if condition is not met.
Example
SELECT count(1) FROM stock_price WHERE assert(price > 0.0);
SELECT count(1) FROM stock_price WHERE assert(price > 0.0, 'price MUST be more than 0.0')RAISE_ERROR
Signature
raise_error()
raise_error(string errMsg)Description
RAISE_ERROR throws an error.
Example
SELECT product_id, price, raise_error('Found an invalid record') FROM xxx WHERE price < 0.0Timeseries Functions
MOVING_AVG
Signature
moving_avg(NUMBER value, const int windowSize)Description
MOVING_AVG returns moving average of a time series using a given window
Example
SELECT moving_avg(x, 3) FROM (SELECT explode(array(1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0)) as x) series;
> 1.0
> 1.5
> 2.0
> 3.0
> 4.0
> 5.0
> 6.0Other Functions
CONVERT_LABEL
Signature
convert_label(const int|const float)Description
CONVERT_LABEL converts from -1|1 to 0.0f|1.0f, or from 0.0f|1.0f to -1|1.
EACH_TOP_K
Signature
each_top_k(int K, ANY_PRIMITIVE_TYPE group, double cmpKey, *)Description
EACH_TOP_K returns top-K values (or tail-K values when k is less than 0) for each group. Group need to be sorted, assuming CLUSTER BY group.
Example
SELECT
each_top_k(
2, class, score,
class, student -- optional argument(s) to be resulted in addition to rank and score
) as (rank, score, class, student) -- rank and score are resulted by the default
FROM (
SELECT class, score, student
FROM table
CLUSTER BY class -- Mandatory for `each_top_k`
) tGENERATE_SERIES
Signature
generate_series(const int|bigint start, const int|bigint end)Description
GENERATE_SERIES generates a series of values, from start to end, similar to PostgreSQL’s generate_series.
Example
SELECT generate_series(2,4);
> 2
> 3
> 4
SELECT generate_series(5,1,-2);
> 5
> 3
> 1
SELECT generate_series(4,3);
> (no return)
SELECT date_add(current_date(),value),value from (SELECT generate_series(1,3)) t;
> 2018-04-21 1
> 2018-04-22 2
> 2018-04-23 3
WITH input as (
SELECT 1 as c1, 10 as c2, 3 as step
UNION ALL
SELECT 10, 2, -3
)
SELECT generate_series(c1, c2, step) as series
FROM input;
> 1
> 4
> 7
> 10
> 10
> 7
> 4TRY_CAST
Signature
try_cast(ANY src, const string typeName)Description
TRY_CAST explicitly cast a value as a type. Returns null if cast fails.
Example
SELECT try_cast(array(1.0,2.0,3.0), 'array<string>')
SELECT try_cast(map('A',10,'B',20,'C',30), 'map<string,double>')X_RANK
Signature
x_rank(KEY)Description
X_RANK generates a pseudo sequence number starting from 1 for each key.
TO_LIBSVM_FORMAT
Signature
to_libsvm_format(array<string> feautres [, double/integer target, const string options])Description
TO_LIBSVM_FORMAT returns a string representation in the libsvm format.
Example
select to_libsvm_format(array(‘apple:3.4’,‘orange:2.1’));
> 6284535:3.4 8104713:2.1
select to_libsvm_format(array(‘apple:3.4’,‘orange:2.1’), ‘-features 10’);
> 3:2.1 7:3.4
select to_libsvm_format(array(‘7:3.4’,‘3:2.1’), 5.0);
> 5.0 3:2.1 7:3.4